|
Document revision date: 30 March 2001
|
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
OpenVMS RTL Screen Management (SMG$) Manual
The output generated by this Fortran program is shown in Figure SMG-37.
Figure SMG-37 Output Generated by Fortran Program Calling
SMG$READ_KEYSTROKE

| #2 |
1 OPTION TYPE=EXPLICIT
!+
! This VAX BASIC program demonstrates the use of
! SMG$READ_KEYSTROKE to read a keystroke from the terminal.
!
DECLARE LONG kb_id, ret_status, term_code, I, timer
EXTERNAL SUB LIB$SIGNAL( LONG BY VALUE )
EXTERNAL SUB LIB$STOP( LONG BY VALUE )
EXTERNAL LONG CONSTANT SS$_TIMEOUT
%INCLUDE "$SMGDEF" %FROM %LIBRARY "SYS$LIBRARY:BASIC$STARLET"
EXTERNAL LONG FUNCTION SMG$CREATE_VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD( LONG, STRING )
EXTERNAL LONG FUNCTION SMG$DELETE_VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD( LONG )
EXTERNAL LONG FUNCTION SMG$READ_KEYSTROKE( LONG, LONG, STRING, &
LONG, LONG )
!+
! Prompt the user for the timer value. A value of 0 will cause
! the type ahead buffer to be read.
!-
INPUT "Enter timer value (0 to read typeahead buffer): ";timer
!+
! Establish a SMG connection to SYS$INPUT. Signal any unexpected
! errors.
!-
ret_status = SMG$CREATE_VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD( kb_id, "SYS$INPUT:" )
IF (ret_status AND 1%) = 0% THEN
CALL LIB$SIGNAL( ret_status )
END IF
!+
! Read a keystoke, tell the user what we found.
!-
ret_status = SMG$READ_KEYSTROKE( kb_id, term_code, , timer, )
IF (ret_status <> SS$_TIMEOUT) AND ((ret_status AND 1%) = 0%) THEN
CALL LIB$SIGNAL( ret_status )
END IF
PRINT "term_code = ";term_code
SELECT term_code
CASE 0 TO 31
PRINT "You typed a control character"
CASE 32 TO 127
PRINT "You typed: ";CHR$(term_code)
CASE SMG$K_TRM_PF1 TO SMG$K_TRM_PERIOD
PRINT "You typed one of the keypad keys"
CASE SMG$K_TRM_UP TO SMG$K_TRM_RIGHT
PRINT "You typed one of the cursor positioning keys"
CASE SMG$K_TRM_F6 TO SMG$K_TRM_F20
PRINT "You typed one of the function keys"
CASE SMG$K_TRM_FIND TO SMG$K_TRM_NEXT_SCREEN
PRINT "You typed one of the editing keys"
CASE SMG$K_TRM_TIMEOUT
PRINT "You did not type a key fast enough"
CASE ELSE
PRINT "I'm not sure what key you typed"
END SELECT
!+
! Close the connection to SYS$INPUT, and signal any errors.
!-
ret_status = SMG$DELETE_VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD( kb_id )
IF (ret_status AND 1%) = 0% THEN
CALL LIB$SIGNAL( ret_status )
END IF
END
|
This BASIC program reads a key and returns the
word-terminator-code and the name of the keystroke
entered. One sample of the commands entered and the output generated by
this program is as follows:
$ RUN READ_KEY
Enter the timer value (0 to read type-ahead buffer): ? 9
term_code = 100
You typed: d
|
Note that, in this example, the user entered the keystroke
"d" following the first prompt. The keystroke entered was not
echoed.
SMG$READ_LOCATOR
The Read Locator Information routine reads information from a
DECwindows workstation terminal's locator device (such as a mouse or
tablet).
Format
SMG$READ_LOCATOR keyboard-id ,row-number ,column-number
,word-terminator-code [,timeout] [,parse-routine]
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Arguments
keyboard-id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Keyboard identifier. The keyboard-id argument is the
address of an unsigned longword containing the identifier of the
desired virtual keyboard.
You can create a virtual keyboard by calling the
SMG$CREATE_VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD routine.
row-number
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Row number to which the locator is pointing. The
row-number argument is the address of an unsigned word
that contains the row number of the virtual display at which the locaor
is pointing.
column-number
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Column number to which the locator is pointing. The
column-number argument is the address of an unsigned
word that contains the column number of the virtual display at which
the read is to be performed.
word-terminator-code
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Locator terminator code. The word-terminator-code
argument is the address of an unsigned word into which is written a
code indicating what locator button terminated the read. Locator
terminator codes are of the form SMG$K_TRM_keyname. The key
names are listed in Table 3-1.
timeout
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Timeout count. The optional timeout argument is the
address of a signed longword that contains a number of seconds. If
specified, any character typed before the timeout is returned in the
buffer.
parse-routine
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_unsigned |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Address of a user-supplied parse routine that is called to parse the
locator input. The optional parse-routine argument is
the address of an unsigned longword that contains the parse routine. If
this argument is not specified, ANSI locator input is assumed.
For more information on the parse routine, see Call Format for a Parse
Routine in the Description section.
Description
SMG$READ_LOCATOR reads information from a DECwindows workstation
terminal's locator device. (This routine does not read locator
information from the VT300 series terminals.) A locator device is a
mouse or a tablet. This routine returns the row and column specified by
the locator, as well as the button pressed. This routine assumes the
locator will respond with an ANSI response. If another format is used,
you must specify the parse-routine argument with the
address of a routine that is called to parse the locator response.
Call Format for a Parse Routine
The parse routine is called only if the parse-routine
argument was specified in the SMG$READ_LOCATOR argument list.
The calling format of a parse routine is as follows:
parse-routine keyboard-id ,response ,row ,column ,button
|
The parse routine should return a success status value (0 bit set),
otherwise SMG$READ_LOCATOR terminates without setting the row, column,
or button parameters and returns this same status cvalue.
Arguments
keyboard-id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Keyboard identifier. The keyboard-id argument is an
unsigned longword containing the identifier of the desired virtual
keyboard.
response
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Locator response to be parsed. The response argument
is the address of a descriptor pointing to the response string to be
read.
row
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Receives the row number to which the locator is pointing. The
row argument is an unsigned word that contains the row
number of the virtual display.
column
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Receives the column number to which the locator is pointing. The
column argument is an unsigned word that contains the
column number of the virtual display.
button
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Receives the button that was pressed. The button
argument is an unsigned word that contains the button pressed. Returned
value should be SMG$K_TRM_keyname.
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Normal successful completion.
|
|
SMG$_EOF
|
End of file.
|
|
SMG$_INVARG
|
Invalid argument.
|
|
SMG$_INVDIS_ID
|
Invalid
display-id.
|
|
SMG$_WRONUMARG
|
Wrong number of arguments.
|
SMG$READ_STRING
The Read String routine reads a string from a virtual keyboard.
Format
SMG$READ_STRING keyboard-id ,resultant-string [,prompt-string]
[,maximum-length] [,modifiers] [,timeout] [,terminator-set]
[,resultant-length] [,word-terminator-code] [,display-id]
[,initial-string] [,rendition-set] [,rendition-complement]
[,terminator-string]
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Arguments
keyboard-id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Specifies the virtual keyboard from which input is to be read. The
keyboard-id argument is the address of an unsigned
longword that contains the keyboard identifier.
The keyboard identifier is returned by SMG$CREATE_VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD.
resultant-string
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
String into which the input line is written. The
resultant-string argument is the address of a
descriptor pointing to the string into which the text is written.
prompt-string
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
String used to prompt for the read operation. The
prompt-string argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to the prompt string.
maximum-length
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Specifies the maximum number of characters to be read. The
maximum-length argument is the address of a signed
longword that contains the maximum number of characters to be read. The
maximum valid value for this argument is 512. If omitted, 512 is the
default.
modifiers
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Optional bit mask that specifies optional behavior. The
modifiers argument is the address of an unsigned
longword that contains the flag.
Valid values for modifiers are as follows:
|
TRM$M_TM_CVTLOW
|
Converts lowercase characters to uppercase characters.
|
|
TRM$M_TM_NOECHO
|
Characters entered are not echoed on the screen.
|
|
TRM$M_TM_NOEDIT
|
Advanced editing is disabled for this read operation.
|
|
TRM$M_TM_NORECALL
|
Line recall is disabled.
|
|
TRM$M_TM_PURGE
|
Type-ahead buffer is purged before read is begun.
|
|
TRM$M_TM_TRMNOECHO
|
Termination character, if any, is not displayed.
|
The TRM$ symbols are defined by the $TRMDEF macro/module in system
symbol libraries supplied by Compaq. See the terminal driver section of
the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual for more information on modifiers for read operations.
timeout
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Specifies the number of seconds allowed between the time the prompt is
issued and the completion of the input operation. The
timeout argument is the address of a signed longword
that contains the timeout value.
If timeout is specified, all characters typed before
the expiration time or until a terminate key is entered are returned in
resultant-string. If omitted, the input operation
remains active until a terminator is typed.
terminator-set
| OpenVMS usage: |
unspecified |
| type: |
unspecified |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor, fixed length |
Either a mask that specifies which characters are to be treated as
terminators (short form) or a descriptor pointing to such a mask (long
form). The terminator-set argument is the address of a
descriptor pointing to the mask.
If you want to use terminators with ASCII values in the range 0 to 31,
use the short form, which consists of two longwords. The first longword
is zero, and the second longword is a terminator character bit mask.
You create this mask by setting the bit that corresponds to the ASCII
value of the desired terminator. For example, to specify that Ctrl/A
(ASCII value 1) is a terminator, you set bit 1 in the
terminator-set mask.
To use terminators with ASCII values outside the range 0 to 31, use the
long form. First create a descriptor of this form:
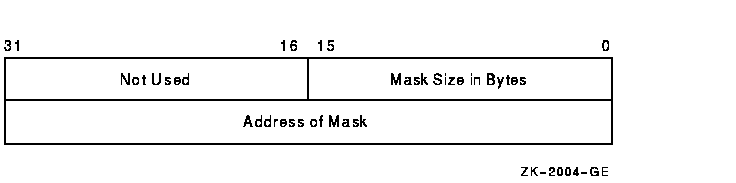
The mask itself has the same format as that of the short form; however,
the long form allows the use of a more comprehensive set of terminator
characters. For example, a mask size of 16 bytes allows any 7-bit ASCII
character to be set as a terminator, while a mask size of 32 bytes
allows any 8-bit character to be set as a terminator. Any mask size
between 1 and 32 bytes is acceptable.
If the terminator mask is all zeros, there are no specified
terminators. In that case, the read terminates when the number of
characters specified in maximum-length has been
transferred or when timeout is reached.
If the terminator-set argument is omitted, the set of
terminators is the OpenVMS default terminator set. For more
information, see the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
resultant-length
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Receives the number of characters read or the maximum size of
resultant-string, whichever is less. The
resultant-length argument is the address of an
unsigned word into which is written the number of characters read or
the maximum size.
word-terminator-code
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Key terminator code. The word-terminator-code argument
is an unsigned word into which is written a code indicating what
character or key terminated the read. Key terminator codes are of the
form SMG$K_TRM_keyname. The key names are listed in
Table 3-1.
display-id
| OpenVMS usage: |
identifier |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Display identifier. The display-id argument is the
address of an unsigned longword that contains the display identifier.
This argument is optional only if you are not using the Screen
Management Facility's output routines.
If you are using the Screen Management Facility input and output
routines, this argument specifies the virtual display in which the
input is to occur. The virtual display specified must be pasted to the
same pasteboard as specified by keyboard-id and must
not be occluded. You cannot accept input from an occluded area of the
virtual display.
In the case of multiple virtual displays, each virtual display has an
associated virtual cursor position. At the same time, there is a single
physical cursor position corresponding to the current location of the
physical cursor. If the display-id argument is
specified, the read begins at the current virtual cursor position in
the specified virtual display. If display-id is
omitted, the read begins in the current physical cursor position. Note
that the length of the prompt-string plus the key
entered is limited to the number of visible columns in the display.
Note
This virtual display must be pasted in column 1 and may not have any
other virtual displays to its right. This restriction applies because
otherwise the occurrence of a Ctrl/R or Ctrl/U would cause the entire
line to be blanked, including any output to the right. To circumvent
this restriction, you may use SMG$REPAINT_LINE to repaint the line when
a Ctrl/R or Ctrl/U is detected.
|
initial-string
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Initial character string. The initial-string argument
is the address of a descriptor pointing to the optional string that
contains the initial characters of the field. The string is written to
the display in the input area, as if it had been entered from the
keyboard. It may be edited in the usual way (provided that
TRM$M_TM_NOEDIT is not set). It must be shorter than
maximum-length, otherwise SMG$READ_STRING returns
immediately without accepting any keyboard input.
rendition-set
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Attribute specifier. The optional rendition-set
argument is the address of a longword bit mask in which each attribute
set causes the corresponding attribute to be set in the display. The
following attributes can be specified using the
rendition-set argument:
|
SMG$M_BLINK
|
Displays blinking characters.
|
|
SMG$M_BOLD
|
Displays characters in higher-than-normal intensity (bolded).
|
|
SMG$M_REVERSE
|
Displays characters in reverse video; that is, using the opposite
default rendition of the virtual display.
|
|
SMG$M_UNDERLINE
|
Displays underlined characters.
|
|
SMG$M_INVISIBLE
|
Specifies invisible characters; that is, the characters exist in the
virtual display but do not appear on the pasteboard.
|
SMG$M_USER1 through
SMG$M_USER8
|
Displays user-defined attributes.
|
The display-id argument must be specified when you use
the rendition-set argument.
rendition-complement
| OpenVMS usage: |
mask_longword |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Attribute complement specifier. The optional
rendition-complement argument is the address of a
longword bit mask in which each attribute set causes the corresponding
attribute to be complemented in the display. All of the attributes that
can be specified with the rendition-set argument can
be complemented with rendition-complement. The
display-id argument must be specified when you use the
rendition-complement argument.
The optional arguments rendition-set and
rendition-complement let the user control the
attributes of the virtual display in which the read is done. The
rendition-set argument sets certain virtual display
attributes, while rendition-complement complements
these attributes. If the same bit is specified in both the
rendition-set and
rendition-complement parameters,
rendition-set is evaluated first, followed by
rendition-complement. By using these two parameters
together, the user can control each virtual display attribute in a
single procedure call. On a single-attribute basis, the user can cause
the following transformations:
| Set |
Complement |
Action |
|
0
|
0
|
Attribute set to default
|
|
1
|
0
|
Attribute on
|
|
0
|
1
|
Attribute set to complement of current setting
|
|
1
|
1
|
Attribute off
|
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)

![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)